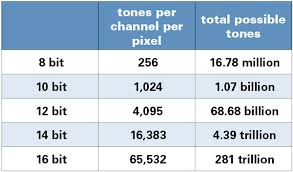
Bit Depth
Bit depth is the number of bits in a sample. This number of bits also determines the resolution of each of the samples. Bit depth’s are used in digital audio. Sampling is the amount of screenshots that are sampled every second. The higher the sample rate, the closer the sound is to being reproduced from the original sound. The relationship between the Bit depth and the sampling is as the bit depth increases the sampling increases. This would also change the bit rate, for example 8 bit and 24 bit.
Bits per pixel (BPP) refers to the amount of the 3 colour channels that are in each pixel and the colour that is represented as a result of this. The more bits there are present, the more colours are presented but this however takes up more memory as more space is needed for each of the colour files.
Monochrome is the color scheme that is used to describe colour that is in gray scale (black and white). Monochrome could be created by removing the colours of an image while editing. In digital graphics, a person may change a picture to monochrome to take up less space as the colour data will no longer be present. This can also be used as an effect. The image below is an example of monochrome where gray is the main colour being used with tints of white and black.

High color is the term that is used to describe something that supports 15 bit or 16 bit. 15 bit colors would use 5 green 5 blue and 5 red bits for each pixels. 16 bit would use 5 green 6 blue and 5 red bits for each pixel.
True color refers to 24 bit images or higher to display and RGB image. True colour is the specification of the colour of a pixel on a display screen using 24-bit value. Typically this allows upto 16 million colours. In the modern day, most displays show only 256 colours (8bit).